概要
SpringBoot的零配置实现是局域java config来实现。在理解springboot之前需要对其充分理解
Spring 配置文件加载机制
- Spring Environment 多数据源机制
Spring的扩展机制
Spring BeanFactory
实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前,修改bean的定义属性。也就是说,Spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置’order’属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。 注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。接口方法的入参是ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,使用该参数,可以获取到相关bean的定义信息
BeanPostProcessor,可以在spring容器实例化bean之后,在执行bean的初始化方法前后,添加一些自己的处理逻辑。这里说的初始化方法,指的是下面两种:
- bean实现了InitializingBean接口,对应的方法为afterPropertiesSet
- 在bean定义的时候,通过init-method设置的方法 注意:BeanPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件并且实例化bean之后执行的。BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序是在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之后
Spring 扩展点
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
- BeanPostProcessor
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor <i>before the target bean gets instantiated</i>.
* The returned bean object may be a proxy to use instead of the target bean,
* effectively suppressing default instantiation of the target bean.
* <p>If a non-null object is returned by this method, the bean creation process
* will be short-circuited. The only further processing applied is the
* {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization} callback from the configured
* {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors}.
* <p>This callback will only be applied to bean definitions with a bean class.
* In particular, it will not be applied to beans with a factory method.
* <p>Post-processors may implement the extended
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor} interface in order
* to predict the type of the bean object that they are going to return here.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to expose instead of a default instance of the target bean,
* or {@code null} to proceed with default instantiation
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessAfterInstantiation
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#hasBeanClass
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Perform operations after the bean has been instantiated, via a constructor or factory method,
* but before Spring property population (from explicit properties or autowiring) occurs.
* <p>This is the ideal callback for performing custom field injection on the given bean
* instance, right before Spring's autowiring kicks in.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}.
* @param bean the bean instance created, with properties not having been set yet
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return {@code true} if properties should be set on the bean; {@code false}
* if property population should be skipped. Normal implementations should return {@code true}.
* Returning {@code false} will also prevent any subsequent InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* instances being invoked on this bean instance.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean. Allows for checking whether all dependencies have been
* satisfied, for example based on a "Required" annotation on bean property setters.
* <p>Also allows for replacing the property values to apply, typically through
* creating a new MutablePropertyValues instance based on the original PropertyValues,
* adding or removing specific values.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code pvs} as-is.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean (with ignored
* dependency types - which the factory handles specifically - already filtered out)
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues
*/
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
Spring Bean 生命周期流程图
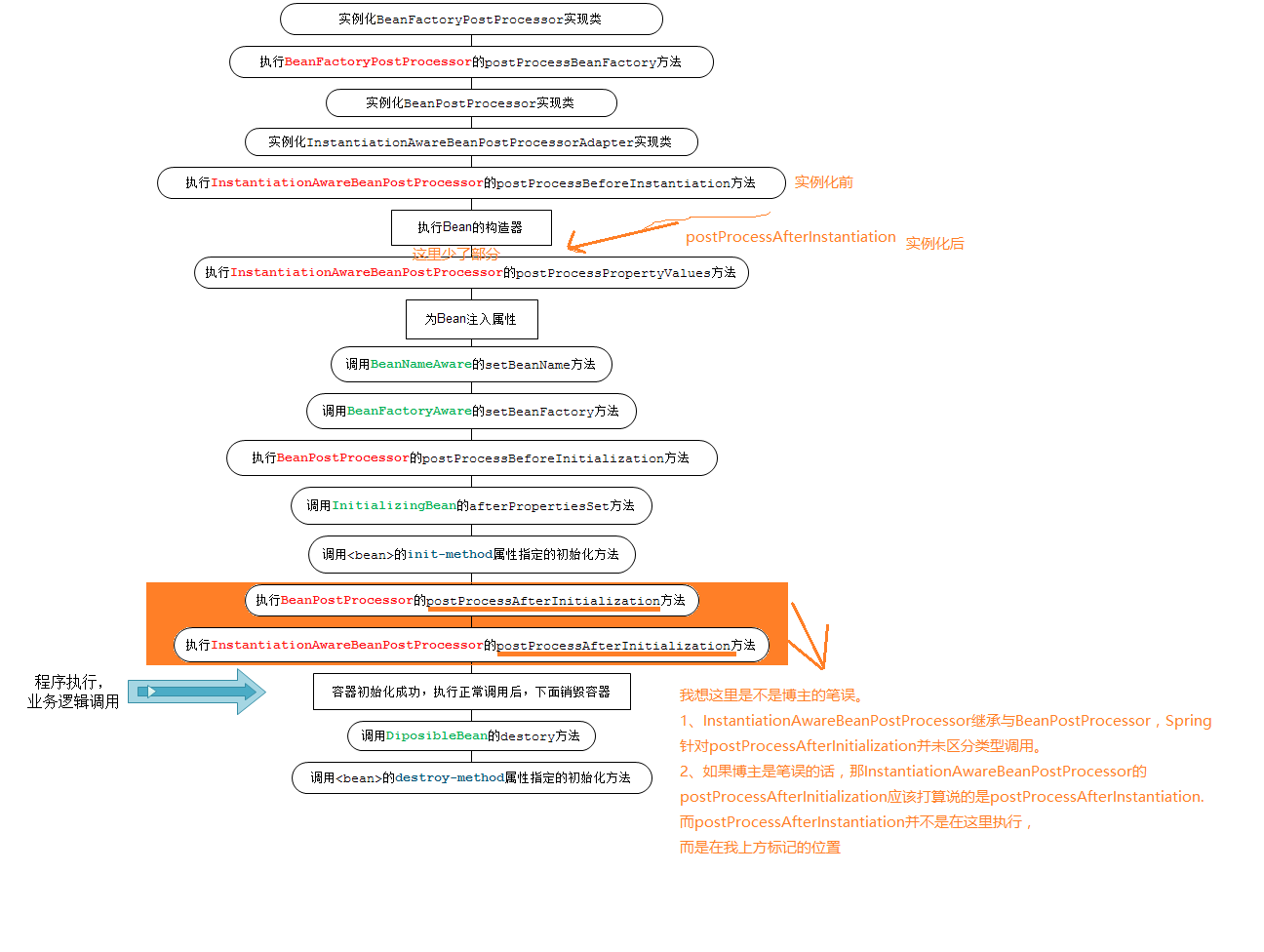
NOTE: 此图中有些说明有误,已经做了说明
Java Config
Spring是如何通过代码配置的方式来替代基于xml配置的bean的声明,两者对比能够快速理解基于java config实现bean声明
核心注解
@Configuration相当于整个xml配置文件,提供注入bean的声明- Spring4.0之二:@Configuration的使用
@Bean类似xml文件</bean>@Import类似xml文件之前</import> Provides functionality equivalent to the {@code} element in Spring XML 支持 Configuration,ImportSelector,ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,regular component classes引入- SpringBoot自动化配置的注解开关原理
PropertySource利用此注解可以动态为environment添加配置数据源
SpringBoot Aop
Spring Aop对目标bean进行代理是通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization()进行的,Spring Aop的代理主要分为三个步骤:获取所有的Advisor,过滤可应用到当前bean的Adivsor和使用Advisor为当前bean生成代理对象
在Spring boot里配置aop非常简单,Spring Boot对AOP的默认配置属性是开启的,也就是说spring.aop.auto属性的值默认是true,我们只要引入了AOP依赖后,默认就已经增加了@EnableAspectJAutoProxy功能,不需要我们在程序启动类上面加入注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy