概述
本文章力图循序渐进的描绘网络相关的知识,进而对网络编程有一个较为整体的理解.本文是在消息通讯分布式架构基础上对NIO,AIO进行整理时,希望自己在实践中,不断加深对其理解,因而需要对所做的东西进行整理,这里附开源项目地址:
- github universe_push
- gitee univers_push
Java NIO
- NIO Channel
- NIO Buffer
- NIO Selector
Netty 核心源码分析
这里不是主要对源码进行说明,主要是为了记录netty实现原理的关键点,这些关键技术点可能成为正常使用netty的核心知识点
BootStrap
服务端的创建过程
示例代码
private void init(){
this.bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
this.bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
this.bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
this.bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) {
}
});
}
绑定开始
protected boolean doStart() throws InterruptedException {
this.channelFuture = this.bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6789)).sync();
return this.channelFuture.isSuccess();
}
NOTE: 服务开启是通过从这个bing方法开始
注册的就是channel注册到eventLoop多路复用器的过程
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
NOTE: 这里register初始的是0,之后会在合适的时机通过selectionKey变更事件关注类型
首次注册等待bind成功,调用firechannelactive方法实现监听accept事件
<!-- head context-->
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
private void readIfIsAutoRead() {
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();
}
}
<!-- AbstractNioChannel -->
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
客户端接入过程
NioEventLoop 轮训
<!-- NioEventLoop -->
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
接收客户端的链接
<!-- NioServerSocketChannel -->
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
//接收客户端的链接
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
try {
ch.close();
} catch (Throwable t2) {
logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
}
}
return 0;
}
触发客户端链接建立事件
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
事件在ServerBootstrapAcceptor中处理
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
<!-- 注册client socketchannel到多路复用器-->
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
修改client channel op_read操作位
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
<!--headContext 方法 -->
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelReadComplete();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
客户端的创建过程
eventLoop注册到Channnel上
这里的注册过程跟serverSocketChannel类似,注册成功之后调用fireRegistered()
- Handler调用连编排
目的是为用户提供一个方便的添加handler的方式
<!--ChannelInitializer --> @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // Normally this method will never be called as handlerAdded(...) should call initChannel(...) and remove // the handler. if (initChannel(ctx)) { // we called initChannel(...) so we need to call now pipeline.fireChannelRegistered() to ensure we not // miss an event. ctx.pipeline().fireChannelRegistered(); } else { // Called initChannel(...) before which is the expected behavior, so just forward the event. ctx.fireChannelRegistered(); } }channelpiple发起connect链接
connect链接是一个outbound事件,该事件会一直传递到headerContext中处理
<!--header context -->
@Override
public void connect(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress,
ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
unsafe.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
<!--NioSocketChannel 发起connect 如果链接暂时没有收到ack回应,则设置interrestOps为OP_CONNECT -->
@Override
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (localAddress != null) {
doBind0(localAddress);
}
boolean success = false;
try {
boolean connected = SocketUtils.connect(javaChannel(), remoteAddress);
if (!connected) {
selectionKey().interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
success = true;
return connected;
} finally {
if (!success) {
doClose();
}
}
}
异步链接结果通知
- 在
NioEventLoop中处理链接成功结果
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
//abstractNioChannel 执行链接成功回调方法
@Override
public final void finishConnect() {
// Note this method is invoked by the event loop only if the connection attempt was
// neither cancelled nor timed out.
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
try {
boolean wasActive = isActive();
doFinishConnect();
fulfillConnectPromise(connectPromise, wasActive);
} catch (Throwable t) {
fulfillConnectPromise(connectPromise, annotateConnectException(t, requestedRemoteAddress));
} finally {
// Check for null as the connectTimeoutFuture is only created if a connectTimeoutMillis > 0 is used
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1770
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
connectPromise = null;
}
}
链接超时设置
//定义链接超时任务
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//如果链接正常,则删除链接超时任务
// Check for null as the connectTimeoutFuture is only created if a connectTimeoutMillis > 0 is used
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1770
if (connectTimeoutFuture != null) {
connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);
}
connectPromise = null;
}
BootStrap总结
以上是对netty的服务端和客户端的创建的简要分析,主要说明各自创建过程中的关键步骤,Netty设计的东西较多,每一块内容都可以独立分析,进而对整个运行流程有一个整体的认知
NOTE: 以下内容主要针对Netty的内部重要模块进行单独分析,进而深入理解Netty是实现高性能网络框架的基本思想
ByteBuf
基本功能
为了解Java nio ByteBuffer的使用性问题,ByteBuf改进功能
- 顺序读操作
- 顺序写操作
- Clear操作
- 查找操作
- 转换标准的ByteBuffer
- 随机读写
类型分类
UnpooledHeapByteBuf
- 实现字节缓冲区动态扩容 这种实现方式依赖其特定的数据结构有专门记录读索引和写索引,实现相互之前互不干扰
//计算缓冲区大小,
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
checkNewCapacity(newCapacity);
//当前字节缓冲区大小
int oldCapacity = array.length;
byte[] oldArray = array;
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
System.arraycopy(oldArray, 0, newArray, 0, oldArray.length);
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);
} else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) {
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
int readerIndex = readerIndex();
// 什么情况下读索引大于缓冲区容量?这个应该是poolHeapBuf中用的,正常情况下扩展空间是不可能出现这个问题的
if (readerIndex < newCapacity) {
int writerIndex = writerIndex();
if (writerIndex > newCapacity) {
writerIndex(writerIndex = newCapacity);
}
System.arraycopy(oldArray, readerIndex, newArray, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex);
} else {
setIndex(newCapacity, newCapacity);
}
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);
}
return this;
}
Channel 和 UnSafe
Channel
channel采用聚合的方式,聚合pipline,channel功能来实现自身功能,公用的方法在父类实现,尽可能实现功能复用 由于channel的功能众多,这里只选取重要的read和write方法分析流程
核心问题
- channel封装了pipline,unsafe,eventloop。pipline的加入实现用户自定义消息处理handler。
- channel 与pipline实现的关系
channel和pipline有部分接口定义是重合的,为什么不考虑在channel的实现方法中直接调用socket api相关接口进行操作,而要使用unsafe在重新包装一层? 这是因为channel在实现connect,read,write方法时需要利用pipline的职责连的方式进行类型aop模式的请求横切,进而实现用户消息自定义handler的实现方式,所以在channel的方法都是先调用pipline中的方法实现 依次回调用户注册的handler,到最后一个handler之后采取调用unsafe真实的实现。
常用方法线程调用分析
- connect
connect操作有pipline发起connect操作,最终在其管理的Context中寻找到HeadContext,其在channel的eventloop中调用unsafe.Connect方法实现连接 - read
读触发是在nio多路复用器在发送读事件发送时,在eventLoop中发起unsafe.read()操作,然后在调用pipline.fireRea进行消息传播 - write
写入消息采用将消息写入到发送缓冲中,发送时将发送消息转为直接内存缓冲,如下
public final void write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer;
if (outboundBuffer == null) {
// If the outboundBuffer is null we know the channel was closed and so
// need to fail the future right away. If it is not null the handling of the rest
// will be done in flush0()
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2362
safeSetFailure(promise, WRITE_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION);
// release message now to prevent resource-leak
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return;
}
int size;
try {
//发送消息过滤,组装成直接内存缓冲
msg = filterOutboundMessage(msg);
size = pipeline.estimatorHandle().size(msg);
if (size < 0) {
size = 0;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return;
}
outboundBuffer.addMessage(msg, size, promise);
}
消息写入发送缓冲中,之后再写入socket的时机选择问题
调用flush方法发送,触发niosocketChannel的doWrite
- 写半包问题 发送缓冲区已经满了,需要设置OP_WRITE标记,下次进行回调发送
channelpipeline 与channelHandler
channelPipline持有channelHandler,channelhandler进行i/o事件拦截处理
- pipline不负责具体i/o事件处理,最终会调用channel和unsafe方法
channelHandler
channelHandler自定义处理器,加入channelContext中,用于处理i/o事件,其衍生出来例如消息编解码器相关的功能 channel相关事件过多,为了方便用户快速定制自己关心的事件,在开发的过程中可以继承channelInboundAdpter,其对用户事件做了默认透传的处理,用户可以针对自己关心的事件方法做覆盖处理 消息解码框架都是依赖channelHandler来实现多协议解析
ByteToMessageDecoder
解码器默认一个规则,如果用户读取到的不是完整包,在读之前需要markreaderIndex,下次解包时需要复位操作
/**
* Get {@code numElements} out of the {@link CodecOutputList} and forward these through the pipeline.
*/
static void fireChannelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CodecOutputList msgs, int numElements) {
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i ++) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msgs.getUnsafe(i));
}
}
NOTE: 这里在进行完消息解码后,是将解码后的list,遍历进行发送,效率较为低下
- CodecOutputList
消息解码重新设计了一个集合池,用来分配与回收list,方便快速解码过程中对象的重复创建于销毁
MessageToByteEncoder
NOTE: 由于用户传递过来的消息一般是对象,对数据进行编码过程中设计到泛型的实际类型获取
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the given message should be handled. If {@code false} it will be passed to the next
* {@link ChannelOutboundHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
*/
public boolean acceptOutboundMessage(Object msg) throws Exception {
return matcher.match(msg);
}
//寻找实际的参数类型
private static Class<?> find0(
final Object object, Class<?> parametrizedSuperclass, String typeParamName) {
final Class<?> thisClass = object.getClass();
Class<?> currentClass = thisClass;
for (;;) {
if (currentClass.getSuperclass() == parametrizedSuperclass) {
int typeParamIndex = -1;
TypeVariable<?>[] typeParams = currentClass.getSuperclass().getTypeParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < typeParams.length; i ++) {
if (typeParamName.equals(typeParams[i].getName())) {
typeParamIndex = i;
break;
}
}
if (typeParamIndex < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"unknown type parameter '" + typeParamName + "': " + parametrizedSuperclass);
}
Type genericSuperType = currentClass.getGenericSuperclass();
if (!(genericSuperType instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
return Object.class;
}
Type[] actualTypeParams = ((ParameterizedType) genericSuperType).getActualTypeArguments();
Type actualTypeParam = actualTypeParams[typeParamIndex];
if (actualTypeParam instanceof ParameterizedType) {
actualTypeParam = ((ParameterizedType) actualTypeParam).getRawType();
}
if (actualTypeParam instanceof Class) {
return (Class<?>) actualTypeParam;
}
if (actualTypeParam instanceof GenericArrayType) {
Type componentType = ((GenericArrayType) actualTypeParam).getGenericComponentType();
if (componentType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
componentType = ((ParameterizedType) componentType).getRawType();
}
if (componentType instanceof Class) {
return Array.newInstance((Class<?>) componentType, 0).getClass();
}
}
if (actualTypeParam instanceof TypeVariable) {
// Resolved type parameter points to another type parameter.
TypeVariable<?> v = (TypeVariable<?>) actualTypeParam;
currentClass = thisClass;
if (!(v.getGenericDeclaration() instanceof Class)) {
return Object.class;
}
parametrizedSuperclass = (Class<?>) v.getGenericDeclaration();
typeParamName = v.getName();
if (parametrizedSuperclass.isAssignableFrom(thisClass)) {
continue;
} else {
return Object.class;
}
}
return fail(thisClass, typeParamName);
}
currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass();
if (currentClass == null) {
return fail(thisClass, typeParamName);
}
}
}
Netty线程模型
NOTE: Netty独有的线程模型是实现高性能异步io的基础,在分析事件传递的过程中,一定要清楚知道该事件执行在那个线程执行,在开发过程中对任务执行要明确其在那个线程执行,是否需要进行必要同步 同一任务操作尽量减少线程切换,实现无锁话设计
- 当前在执行channelCtx.fire相关操作时,事件在pipline中传递过程中,找到真正执行的channelContext之后,都会讲任务抛到channel绑定的eventloop中执行,确保同一channel的相关操作在同一个线程中执行
- 无锁化设计
NioEventLoopGroup
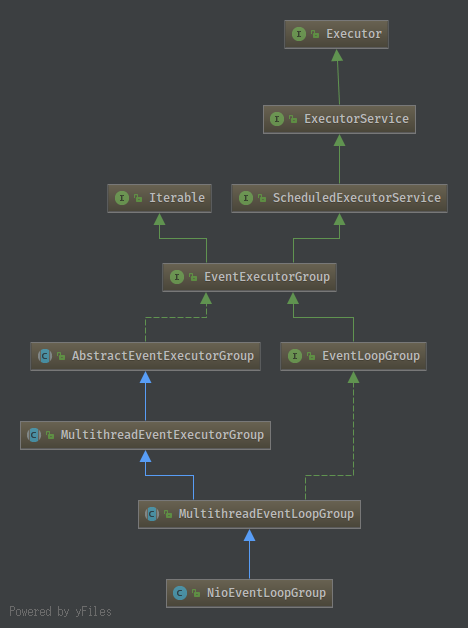
管理NioEventLoop的线程组,调用group里面的方法实际通过next方法查找其管理的eventLoop执行其后的操作,相当有EventLoop线程池管理组工具
-
EventLoopGroup EventLoopGroup核心构造还是初始化EventLoop数组,组件chooser对象以便以后可以随机选取一个eventloop,本质还是调用eventloop中核心方法
-
创建EventLoop的核心参数executes,所有创建的eventloop都是基于此Excutor产生的线程
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor { private final ThreadFactory threadFactory; public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) { if (threadFactory == null) { throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory"); } this.threadFactory = threadFactory; } @Override public void execute(Runnable command) { threadFactory.newThread(command).start(); } }
NioEventLoop
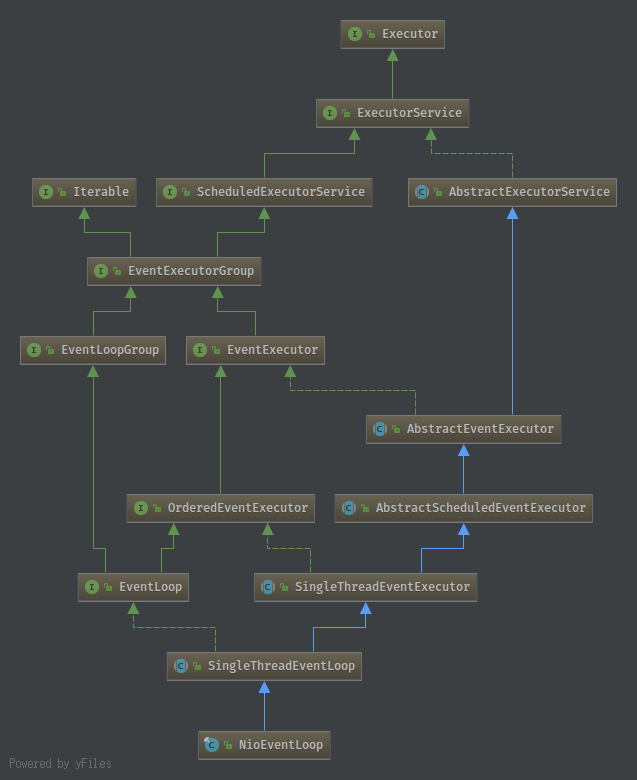
NOTE: 从图中可以看出,在抽象类增加功能时,新定义的接口继承抽象类的接口,增加新的方法实现,为新的抽象类添加新的功能
- 两者都实现了EventLoopGroup,从而实现group能够最终由NioEventLoop实现
- 实现Exexute方法,执行任务,所有的schedule方法都是基于此来实现的
@Override public void execute(Runnable task) { if (task == null) { throw new NullPointerException("task"); } boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop(); //如果是在当前eventloop线程中,将任务加入到队列中,等待执行 addTask(task); //判断是否在当前eventLoop线程中执行 if (!inEventLoop) { //如果不在当前eventloop线程中,则从新开启一个线程 startThread(); if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) { reject(); } } if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) { wakeup(inEventLoop); } }
NOTE: 每个NioEventLoop原则上在在启动任务执行后,只会创建并管理这一个线程,该线程常驻,通过不断轮询执行i/o与用户自定义task任务
- 启动常驻线程后,不断轮询
private void doStartThread() { assert thread == null; executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); if (interrupted) { thread.interrupt(); } boolean success = false; updateLastExecutionTime(); try { SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run(); success = true; } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t); } finally { for (;;) { int oldState = state; if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet( SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) { break; } } // Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop. if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) { logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " + SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must be called " + "before run() implementation terminates."); } try { // Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks. for (;;) { if (confirmShutdown()) { break; } } } finally { try { cleanup(); } finally { STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED); threadLock.release(); if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) { logger.warn( "An event executor terminated with " + "non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')'); } terminationFuture.setSuccess(null); } } } } }); } - SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run()方法执行i/o,task任务
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' is always evaluated
// before calling 'selector.wakeup()' to reduce the wake-up
// overhead. (Selector.wakeup() is an expensive operation.)
//
// However, there is a race condition in this approach.
// The race condition is triggered when 'wakenUp' is set to
// true too early.
//
// 'wakenUp' is set to true too early if:
// 1) Selector is waken up between 'wakenUp.set(false)' and
// 'selector.select(...)'. (BAD)
// 2) Selector is waken up between 'selector.select(...)' and
// 'if (wakenUp.get()) { ... }'. (OK)
//
// In the first case, 'wakenUp' is set to true and the
// following 'selector.select(...)' will wake up immediately.
// Until 'wakenUp' is set to false again in the next round,
// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' will fail, and therefore
// any attempt to wake up the Selector will fail, too, causing
// the following 'selector.select(...)' call to block
// unnecessarily.
//
// To fix this problem, we wake up the selector again if wakenUp
// is true immediately after selector.select(...).
// It is inefficient in that it wakes up the selector for both
// the first case (BAD - wake-up required) and the second case
// (OK - no wake-up required).
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
// fall through
default:
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
- NIO 实现原理
NIO基于Epoll的实现,主要要包括epoll_create, epoll_ctl,epoll_wait三个核心系统调用,selector实现关键是在select(),wakeup()是如何实现的 NIO中的Selector封装了底层的系统调用,其中wakeup用于唤醒阻塞在select方法上的线程,它的实现很简单,在linux上就是创建一 个管道并加入poll的fd集合,wakeup就是往管道里写一个字节,那么阻塞的poll方法有数据可读就立即返回 wakeup调用了EPollArrayWrapper的interrupt方法
public void interrupt()
{
interrupt(outgoingInterruptFD);
}
实际调用的是interrupt(fd)的native方法,查看EPollArrayWrapper.c可见清晰的write系统调用:
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_EPollArrayWrapper_interrupt(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jint fd)
{
int fakebuf[1];
fakebuf[0] = 1;
if (write(fd, fakebuf, 1) < 0) {
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env,"write to interrupt fd failed");
}
}
EventLoop总结
这里面的核心逻辑还是对select i/o模型的理解,越是对底层了解越深入,就能越理解netty开发者对nio 的一些相关优化。对底层的不断梳理过程其实是对基础知识的考验,更加能说明基础的牢固性决定一个人的上限有多高 理解基础的架构决定在排查问题的跟踪深度
Future 和Promise
future模型提供了一种异步通知回调的功能,i/o线程在处理完事件后,会尝试唤醒在该对象上的等待线程,netty的future机制主要使用Object的wait和notify机制来实现
- wait方法
@Override public Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException { if (isDone()) { return this; } if (Thread.interrupted()) { throw new InterruptedException(toString()); } checkDeadLock(); synchronized (this) { while (!isDone()) { incWaiters(); try { wait(); } finally { decWaiters(); } } } return this; } - notify
private synchronized void checkNotifyWaiters() { if (waiters > 0) { notifyAll(); } } - 禁止在I/o线程中调用await方法进行等待,future机制是协调不同线程之间的通信
总结
- 各个模块的设计功能清晰,但是Netty能够合理利用各个模块进行组装才是设计核心,充分展示了面向接口编程的思想
- 利用对象组合的思想封装功能,首先要清楚改类需要实现那些功能需要那些模块,然后在进行合理组装
- 良好的线程模型是关键,一定要清楚代码运行线程信息,在那个线程运行,是否有同步,死锁
- 对运行过程中对象的创建信息如个数,都要清楚